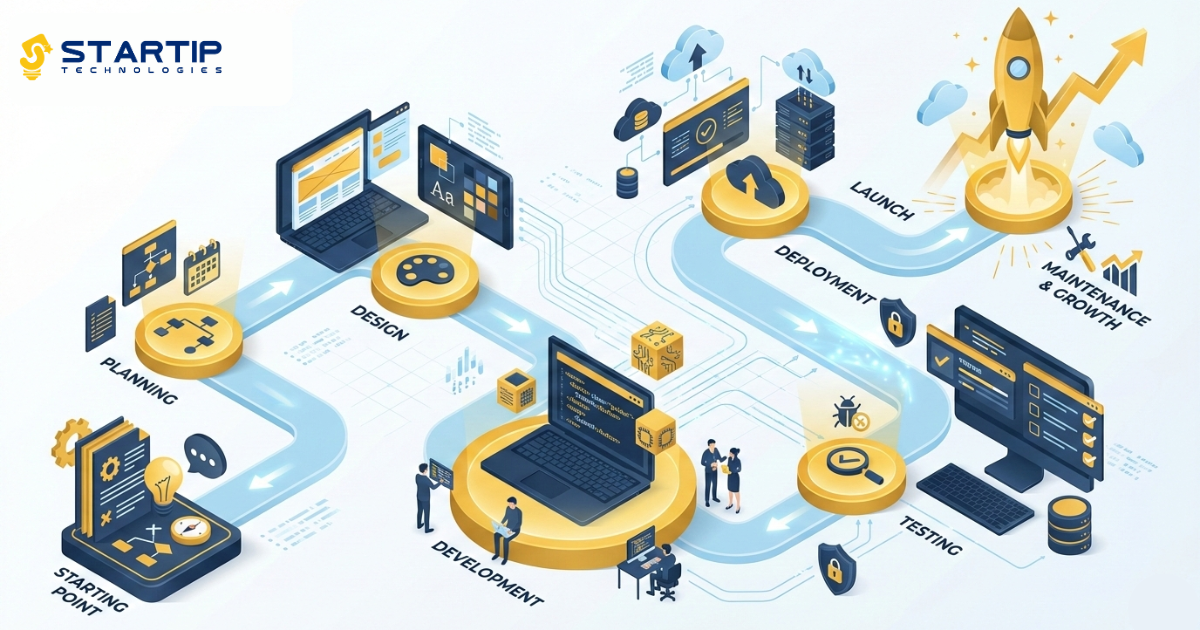
Developing Oxzep7 software successfully is a major challenge in today’s tech world. In fact, up to 75% of software projects fail to meet their goals, timelines, and budgets, often delivering less than what users expect. This highlights how critical it is to approach software development with a clear plan, the right team, and a structured process.
In this guide, we will walk you through how to develop Oxzep7 software from concept to launch — including planning, architecture, development stages, and best practices — so you can build a product that works, scales, and succeeds in the market.
1. What Is Oxzep7 Software?
Before you begin development, it’s important to clearly define what Oxzep7 software is — both functionally and strategically.
Oxzep7 software refers to a specialized application designed to perform specific tasks for businesses or users. While the exact domain of Oxzep7 may vary (e.g., workflow automation, analytics, integration tooling), the core idea is to build a functional and scalable software product that solves real user problems.
Successful software isn’t just coded well — it solves a validated problem, serves a target audience, and fits within technical and business constraints.
2. Pre-Development Planning: Strategy Is Everything
Define Your Product Vision
Start by answering these questions:
- What is Oxzep7 supposed to do?
- Who is the target user?
- What problem does it solve better than alternative solutions?
A clear vision stops you from building features people don’t need — a common reason projects fail.
Conduct Market Research
Understand your competition and user needs:
- What are existing tools lacking?
- What do users complain about?
- What features are essential vs optional?
This helps shape a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a basic version you can develop quickly and test in the real world.
3. Requirements Gathering and Documentation
Good requirements are the foundation of successful development. Poor requirements are one of the top causes of software failure.
Create Clear Functional Specifications
List what the software must do — e.g.:
- User authentication
- Dashboard views
- Data export/import
Non-Functional Requirements
These define software quality, such as:
- Performance benchmarks
- Security standards
- Cross-device compatibility
- Scalability expectations
Well-documented requirements reduce uncertainty for developers and stakeholders alike.
4. Choosing the Right Development Approach
There are several software development methodologies, including:
Agile Development
- Iterative and flexible
- Frequent releases and feedback loops
- Great for changing requirements
Waterfall Model
- Linear and planned upfront
- Works for projects with clearly defined scopes
Most modern teams favor Agile for complex products like Oxzep7, because it allows continuous improvement and faster failure discovery.
5. Designing the Architecture
The software architecture determines how components will interact — and it should be robust, flexible, and scalable.
Core Architectural Decisions
- Monolithic vs microservices:
Microservices allow individual components to update independently. - Database planning:
Choose SQL (structured data) or NoSQL (flexible, unstructured) based on your data needs. - Cloud infrastructure:
AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure offer scalability and global reach.
The architecture should also focus on:
- Maintainability
- Performance
- Security
Planning here saves huge costs later.
6. UI/UX Design: Interface and Interaction
A great product needs more than functionality — it must be easy and delightful to use.
User Experience (UX)
UX focuses on:
- Logical user journeys
- Easy navigation
- Clear workflows
- Minimal clicks to complete tasks
User Interface (UI)
UI focuses on:
- Visual elements
- Fonts and colors
- Icons and layout
- Consistency and branding
Good UI and UX together ensure users find your Oxzep7 software intuitive and satisfying, reducing support costs and increasing adoption.
7. Development: Building the Product
During coding, the team writes software using the chosen technologies and frameworks.
Front-End Development
This is what users interact with — the visual side:
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue
Back-End Development
This handles logic, data, and server tasks:
- Node.js, Python, Ruby, Java, Go
- API creation
- Business logic processor
Database Integration
Clean and efficient database schemas ensure faster data access and fewer bottlenecks.
8. Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing is essential — poor quality and bugs can cripple a product and kill user trust.
Types of Testing
- Unit testing: checks individual components
- Integration testing: ensures components work together
- System testing: full system evaluation
- User acceptance testing (UAT): real users test core functions
Failure due to poor testing is extremely common, and rigorous testing saves major issues post-launch.
9. Deployment and Release Strategy
Releasing software doesn’t happen all at once — it requires careful planning:
Staging Environment
Before production, test in an environment that mirrors real usage.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Automates testing and deployment, making releases safer and faster.
Rollout Plan
Decide whether to:
- Release to all users at once
- Use phased or regional rollouts
10. Post-Launch: Monitoring and Maintenance
Once the software is live, the real work begins.
- Bug Fixes and Update: Users will uncover issues that weren’t seen in testing.
- Performance Monitoring: Tools like Grafana, New Relic, or DataDog help track performance.
- User Feedback Loop: Continual input from users helps improve future releases.
11. Security Considerations
Security should be embedded in every stage:
- Secure coding guidelines
- Input validation
- Authentication and authorization
- Data encryption both at rest and in transit
12. Tips for Avoiding Common Development Pitfalls
Based on industry trends, challenges often arise from non-technical problems such as unclear goals and poor planning. Nearly half of software projects fail due to these issues. Here’s how to avoid them:
- Tip 1: Align All Stakeholders: Everyone should agree on objectives, timelines, and deliverables before coding begins.
- Tip 2: Start with an MVP: Focus on the essential features first, then expand based on real user feedback.
- Tip 3: Build a Balanced Team: Include developers, designers, QA engineers, and project managers.
- Tip 4: Maintain Clear Communication: Use tools like Slack, Jira, and Confluence to keep everyone aligned.
- Tip 5: Keep Documentation Updated: Documentation saves time and helps new team members onboard quickly.
Conclusion
Developing Oxzep7 software doesn’t have to be overwhelming if you follow a structured approach: plan deliberately, design user-centric interfaces, test thoroughly, and iterate quickly based on feedback. In a world where most software projects fail to meet expectations, strong strategy and process are your biggest assets.
With the right team, tools, and method, you can build a successful, scalable, and secure Oxzep7 application that stands out in the market. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, these principles will guide you from concept to launch — and beyond.